The Institute for Large Area Microelectronics (IGM) is currently doing research on the extension and transfer of various technologies originally developed for flat panel display technology into completely new fields of application. Such examples are the use of liquid crystals for future 6G mobile networks and the use of thin film technology for quantum sensor technology.
6G-LICRIS Project
Research topic of the BMBF funded joint research project 6G-LICRIS (Liquid Crystal Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces for 6G Mobile Networks) is the integration of liquid crystal based intelligent, reflective surfaces in future 6G mobile networks. The most famous example of today’s use of liquid crystals as light modulators are the AM LCD (Active Matrix Liquid Crystal Display) flat panel displays. Further developments in liquid crystal chemistry and increasingly higher frequencies in mobile networks make the liquid crystals also interesting for the phase modulation of radio waves. The RIS (Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces) shall improve network coverage by controlled reflection of radio waves and reduce power consumption compared to the usage of repeaters. The working principle is comparable to a two dimensional phased array antenna, where the phase difference between the single elements is influenced by locally controlling the orientation of liquid crystal molecules. First tasks of IGM are development and optimization of manufacturing processes for the LC based RIS elements and integration with an adapted (active) matrix technology. This is followed by the development of a dedicated addressing system and finalized by realization of complete RIS modules at IGM for characterization and network demonstrator integration at the project partners sites.
Research Training Group (GRK2642): Quantum Sensor
Within the Research Training Group (GRK2642) "Quantum Sensor", thin-film components, such as those used for pixel control and compensation circuits in active matrix OLED displays, are researched and further optimized at the IGM, and integrated sensor, amplifier and readout circuits for light sensors and optogalvanic trace gas sensors are developed on this basis. A related conference paper at the SID Display Week 2023 entitled "Ultraviolet Photodetectors and Readout Based on a-IGZO Semiconductor Technologyʺ was awarded the "Distinguished Student Paper Award" and published in an extended version in the "Journal of the Society for Information Display".
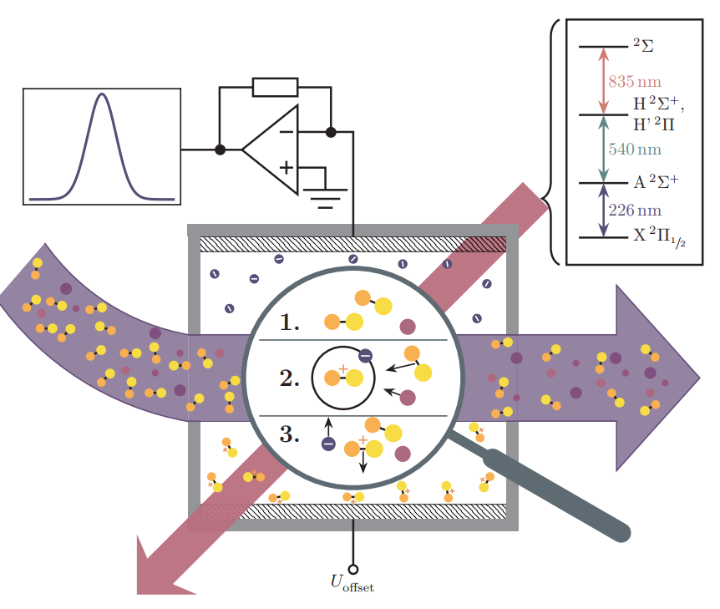
In case of optogalvanic trace gas sensors, for example, nitric oxide (NO) molecules in gas cells are excited to Rydberg states and subsequently ionized by collisions with the background gas. The charges are guided to electrodes and detected by current measurements. Thin film technology can be used to realize the electrical readout (electrode + transimpedance amplifier) on the vapor cell wall.
| Attachments |
|---|